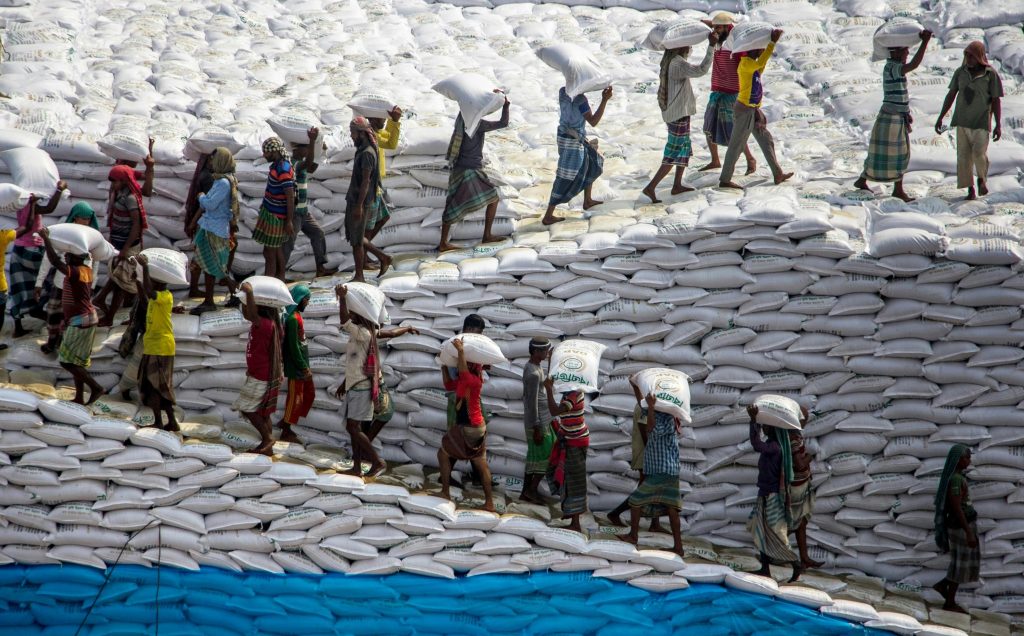
Payroll in HR (Human Resources) refers to the process of calculating, distributing, and managing employee wages and salaries. It includes tasks like tracking work hours, Working Days, deciding pay rates, calculating taxes and deductions, issuing payments, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and company policies.
Payroll is essential in HR because it directly impacts employee satisfaction, legal compliance, and the overall financial health of the organization.
Here we will see some key components of payroll in HR-
1. Employee Data Collection: It is Gathering data on hours worked, Day worked, overtime, leave, and other time-off details, according to that we process the salary for example is your September Salary is 3000 then per day as per attendance you are getting 100 if you are absent any of day you will paid as LOP.
2.Compensation Calculations: Compensation i.e CTC (Cost to company). it is Calculation of gross and net wages based on work hours or Days like calculation of salaries, overtime, bonuses, and commissions.
3.Deductions: In Payroll there are some statutory deduction like income tax, social security, health insurance, retirement contributions etc which we need to consider while processing payroll.
4.Distribution of Pay: Managing the timely disbursement of pay through direct deposits, checks, or other payment methods. There are certain deadline as per the Wages ACT where the salary credit date is specific day is defined for every month.
5.Compliance: Adhering to legal requirements such as minimum wage laws, overtime regulations, and tax filing. Non-compliance can lead to penalties for the organization. There are some compliance which popular in India is PF,ESIC,TDS,LWF
6.Record Keeping: Maintaining payroll records for audits, employee references, and other administrative needs. It is very confidential and sensitive information which the Payroll processor has to maintain.
7.Reporting: Generating payroll reports for financial and operational analysis, basis on that report we disburse the salary to employee’s account.

A Comprehensive Guide to Payroll Management
In India, Human Resource (HR) Payroll plays a pivotal role in managing employee compensation, maintaining compliance, and ensuring efficient business operations. HR Payroll is not just a monthly routine of disbursing employee salaries; it involves complex calculations, deductions, tax compliance, record-keeping, and more. With India’s unique regulatory landscape and employment laws, payroll management becomes a key function of HR, impacting employee satisfaction and legal compliance alike.
Some Key Components of HR Payroll in India in details
In India, payroll management involves multiple layers of calculations and statutory deductions. Here are the primary components:
1. Gross Salary Calculation :- The gross salary is the total income of an employee before any deductions. It includes various components such as the basic salary, allowances (like HRA, travel, and medical allowances), bonuses, and incentives.
2. Deductions:- India has several statutory deductions mandated by law. Some of these deductions include
Provident Fund (PF): Both employee and employer contribute 12% of the basic salary (capped at ₹15,000 per month unless opted otherwise). The Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) administers this.
Employee State Insurance (ESI): For companies with more than 10 employees earning less than ₹21,000 per month, ESI contributions are mandatory. Employers contribute 3.25%, while employees contribute 0.75% of their salary.
Professional Tax (PT): This state-level tax varies across states. It’s a nominal deduction ranging from ₹200 to ₹2,500 per annum, depending on the salary slab
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): Based on an employee’s salary, income tax is deducted as per income tax slabs. Employers must compute TDS based on employee declarations of income and investments.
3. Allowances
Allowances are additional amounts paid over the basic salary to cover various expenses. Some common allowances include:
House Rent Allowance (HRA): An allowance to cover the cost of renting a house.
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): For employees’ travel expenses during leave.
Conveyance Allowance: To cover travel expenses to and from work.
4. Bonuses and Incentives:-Many companies offer bonuses, like Diwali or performance-based incentives, as part of the payroll structure. Bonuses are taxable, and employers need to ensure they are processed accurately.
5. Reimbursements:- Companies often provide reimbursements for medical, travel, or meal expenses, which may or may not be part of the taxable income depending on the eligibility and compliance with reimbursement policies.
Steps in the Payroll Process
Payroll processing in India typically follows a structured sequence to ensure all calculations, records, and deductions are accurate.
1. Employee Onboarding and Data Collection:-This step involves gathering and recording employee data like bank details, PAN, Aadhaar, salary structure, and other necessary documents
2. Attendance and Time Tracking:-HR collects data on work hours, overtime, leaves, and attendance, which directly impacts payroll calculations, especially in industries where wages are time-dependent
3. Salary Calculation:-Payroll software is often used to automate calculations of gross pay, deductions, and allowances based on predefined parameters. This ensures speed and accuracy in salary computation.
4. Tax and Statutory Deductions:-Employers calculate PF, ESI, PT, and TDS based on each employee’s salary. Employers also calculate TDS based on employee declarations for investments and other deductions.
5. Payroll Disbursement:-Once verified, salaries are deposited into employees’ bank accounts. Employers generate salary slips for each employee, detailing their pay structure, deductions, and net salary.
6. Payroll Record-Keeping and Compliance:-Indian regulations require companies to maintain accurate payroll records for audit and compliance purposes. Failure to comply can lead to fines and penalties.

Regulatory Compliance in Indian Payroll
1. Income Tax Act: Employers must deduct TDS according to the income tax slab and deposit it with the Income Tax Department monthly. Annual TDS returns must be filed as well.
2. Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952: The EPF Act mandates PF contributions and adherence to rules on withdrawals and loans
3.Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948: ESI contributions are compulsory for eligible employees and employers, contributing to employee health and welfare.
4.Minimum Wages Act, 1948: Employers must ensure they pay employees according to the minimum wage rates set by the government.
5.Payment of Bonus Act, 1965: Companies with 20 or more employees are required to pay an annual bonus to eligible employees, generally 8.33% to 20% of their basic salary.
The Role of Payroll Software in Streamlining Payroll
Payroll software is a valuable tool for HR departments in India, offering automation, accuracy, and compliance. By reducing manual calculations, payroll software minimizes errors and provides a centralized system for payroll management. Advanced payroll software can calculate deductions, generate payslips, maintain records, and provide comprehensive tax reports, ensuring compliance with legal requirements
Challenges in Payroll Management in India
Managing payroll in India can be complex due to varying state regulations, dynamic tax laws, and constant updates in labor laws. Some of the common challenges include
A.Compliance with Changing Laws: Indian payroll regulations are subject to frequent changes, and staying updated is critical.
B.Handling Employee Diversity: Different employment types (full-time, part-time, contract) may require distinct payroll handling
C.Data Security: Payroll data is sensitive, and safeguarding employee data from breaches is essential.
D.Manual Processing Errors: Human errors in manual payroll processing can lead to inaccuracies, penalties, and compliance issues
310848 45457woah i like yur web site. It actually helped me with the information i wus seeking for. Appcriciate it, will bookmark. 833574
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
专业构建与管理谷歌站群网络,助力品牌实现全域流量的强势增长。谷歌站群
专业构建与管理谷歌站群网络,助力品牌实现全域流量的强势增长。谷歌站群
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/en-IN/register-person?ref=A80YTPZ1
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Yo, heard about 55wincom from a buddy. Thinkin’ of checkin’ it out. Heard they got some decent odds. Wish me luck! Gonna give 55wincom a try!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Yo, getting into Jiliok Casino is a breeze! The login process is stupid simple. Just remember your credentials and you’re golden. They’ve got a decent selection of Jili games so if you’re a fan, it’s worth a peek. Log in here: jiliokcasinologin
204263 403159Wohh just what I was seeking for, thanks for putting up. 200708
Been playing on Codwin for a while now, and they’ve always been solid. Pretty good promotions too. Give em a look codwin.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
453216 930516Hey! Excellent post! Please do tell us when we can see a follow up! 882132